TL;DR Libra is a zero-knowledge proof protocol that achieves extremely fast prover time and succinct proof size and verification time. Not only does it have good complexity in terms of asymptotics, but also its actual running time is well within the bounds of enabling realistic applications. It can be applied in areas such as blockchain technology and privacy-preserving smart contracts. It is currently being implemented by Oasis Labs.
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) are cryptographic protocols between two parties, a prover and a verifier, in which the prover wants to convince the verifier about the validity of a statement without leaking any extra information beyond the fact that the statement is true. For example, the verifier could confirm that the prover computes some functions ‘F(w) = y’ correctly even without knowing the input ‘w.’ Since they were first introduced by Goldwasser et al. [1], ZKP protocols have evolved from pure theoretical constructs to practical implementations. They have achieved proof sizes of just hundreds of bytes and verification times of a few milliseconds, regardless of the size of the statement being proved. Due to this successful transition to practice, ZKP protocols have found numerous applications, not only in the traditional computation delegation setting, but also in blockchain settings such as providing privacy of transactions in deployed cryptocurrencies (e.g., Zcash [2]).
And a ZKP protocol must meet three criteria: completeness, soundness, zero knowledge. See below for an explanation.
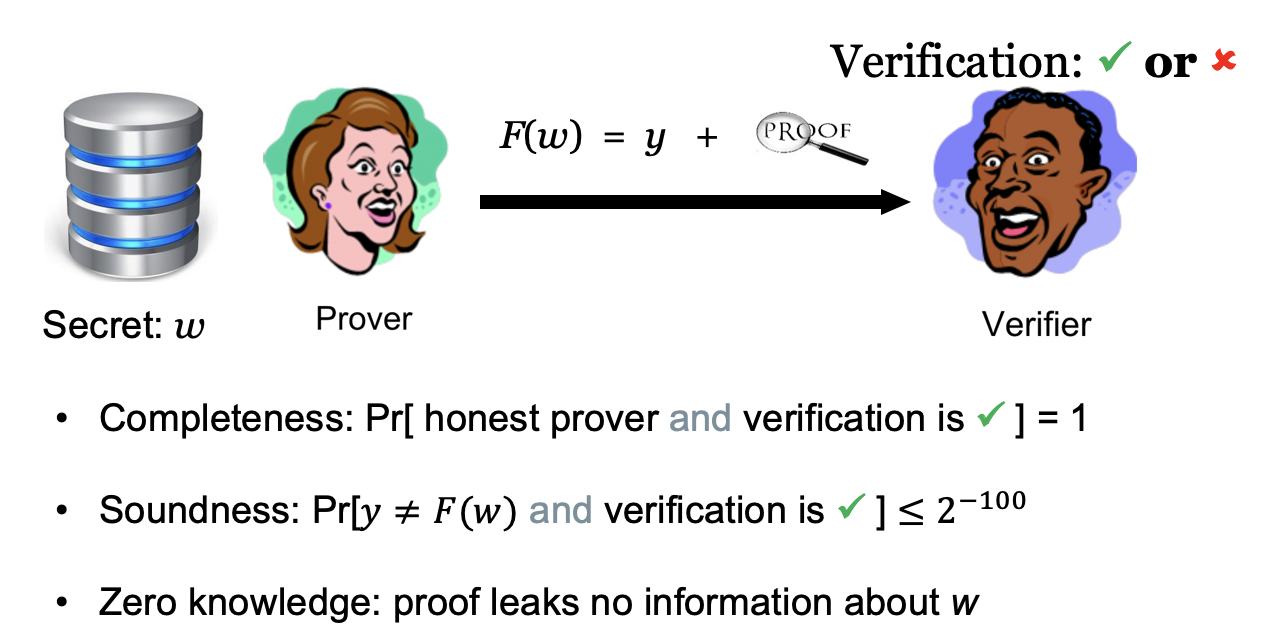
An explanation of the formal security requirements for zero-knowledge proofs.
Despite such progress in practical implementations, ZKP protocols are still notoriously hard to scale for large statements due to a particularly high overhead on generating the proof. For most protocols, this is primarily because the prover has to perform a large number of cryptographic operations, such as exponentiation in an elliptic curve group. And to make things worse, the asymptotic complexity of computing the proof is typically more than linear, e.g., ‘O(C log C)’ or even ‘O(C log^2 C),’ where ‘C’ is the size of the statement. Therefore designing ZKP protocols that enjoy linear prover time as well as succinct proof size and verification time is an open problem.
Resolving this problem has significant practical implications. For example, we could generate the proof for larger statements on blockchain within acceptable time bound, which could also further extend the privacy of transactions or smart contract.
Enter Libra (not affiliated with the Libra project launched by Facebook)
Originally proposed in a paper from early 2019, Libra solves the problem described above with a zero-knowledge proof protocol that has three important properties:
The underlying protocols of Libra are an interactive proof protocol proposed by Goldwasser, Kalai, and Rothblum, in [5] (referred to as GKR protocol), and the verifiable polynomial delegation (VPD) scheme proposed by Zhang et al. in [6]. It comes with one-time trusted setup (not per-statement trusted setup) that depends only on the size of the input (witness) to the statement that is being proved.
In the original GKR protocol, the prover could only generate a proof of the statement without satisfying the zero-knowledge property. That means the verifier could learn secret information of the prover from the proof itself, which we want to avoid. In addition, in the GKR protocol, the computation of the statement is based on the arithmetic layered circuit(layered circuit with only addition and multiplication gates) and the time of the prover to generate the proof is polynomial in the number of gates in this circuit. This is slow if the circuit size is large.
Libra’s contribution is solving these two problems in the GKR protocol and could be summarized as follows:
Table 1 shows a detailed comparison between the asymptotic complexity of Libra and the existing ZKP protocols. A first observation is that Libra has the best prover time among all existing protocols, indicated as row P on the table. In terms of asymptotics, Libra is the only protocol that satisfies all of the following properties simultaneously: linear prover time, succinct verification, and succinct proof size structured circuits. The only other protocol with linear prover time is Bulletproofs whose verification time is linear, even for structured circuits. In the practical front, Bulletproofs’ prover time and verifier time are high due to the large number of cryptographic operations required for every gate of the circuit.
The proof and verification of Libra are also competitive to other protocols. In asymptotic terms, our proof size is only larger than libSNARK and Bulletproofs, and our verification is slower than libSNARK and libSTARK. Compared to Hyrax, which is also based on similar techniques with our work, Libra improves the performance in all aspects with one-time trusted setup.
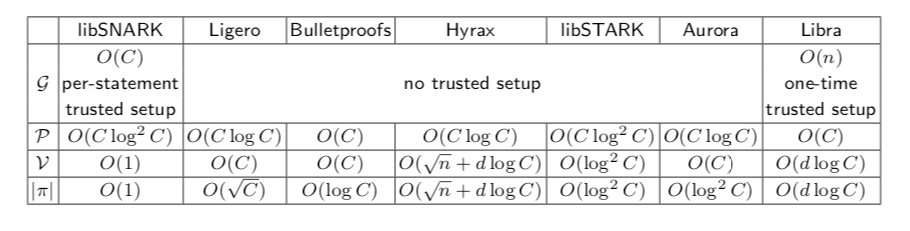
Comparison of Libra to existing ZKP protocols, where (G, P, V, |π|) denote the trusted setup algorithm, the prover algorithm, the verification algorithm and the proof size respectively. Also, C is the size of the circuit with depth d, and n is the size of its input.
Software. We implement Libra, our new zero-knowledge proof protocol, in C++. Our protocol provides an interface that takes as input a generic layered arithmetic circuit and generates a zero-knowledge proof according to the circuit and the input of the circuit. We support a class of 512 bit unsigned integers that improve on the performance of the GMP library in specific cases and use it together with GMP for large numbers and field arithmetic. We use the popular cryptographic library “ate-pairing” on a 254-bit elliptic curve for the bilinear map used in zero-knowledge VPD. We have released the code as an open-source system (https://github.com/sunblaze-ucb/Libra).
Hardware. We run all of the experiments on Amazon EC2 c5.9xlarge instances with 70GB of RAM and Intel Xeon platinum 8124m CPU with 3GHz virtual core. Our current implementation is not parallelized and we only use a single CPU core in the experiments, so we hypothesize that one can further improve the efficiency of the reported numbers. We report the average running time of 10 executions.
Methodology and benchmarks. We compare our GKR protocol to these variants on the benchmarks below:
We report the prover time, proof size and verification time in Figure 1.
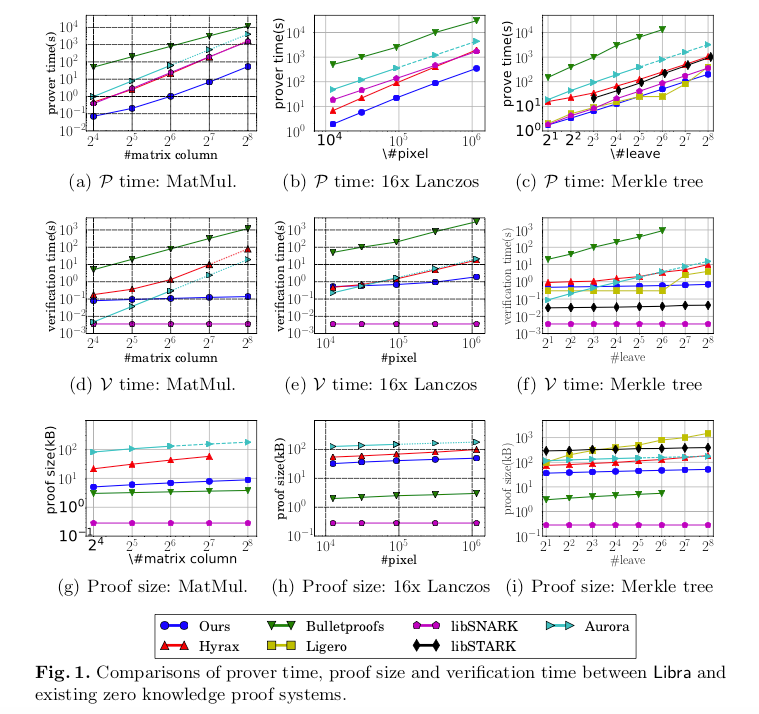
Which brings us to the conclusion. As shown in Figure 1(a)(b)(c), the prover in Libra is the fastest among all systems in all three benchmarks we tested. Figure 1(d)(e)(f) show the verification time. Our verifier is much slower than libSNARK and libSTARK, which runs in 1.8ms and 28-44ms respectively in all the benchmarks. Other than these two systems, the verification time of Libra is faster, as it grows sub-linearly with the circuit size. We report the proof size in Figure 1(g)(h)(i). Our proof size is much bigger than libSNARK and Bulletproof but it is better than Aurora, Hyrax, Ligero and libSTARK.
Immediate Implementation. Tiancheng Xie and Jiaheng Zhang interned at Oasis Labs in summer 2019 and worked to implement Libra. The Oasis Team has plans to further develop it in the future.
Based on the exciting results of Libra we set to solve one vital limitation of our proposal, namely “the trusted setup”. In our new follow up project called “Virgo”, we propose a transparent ZKP protocol with even better prover time and verification time. The proof size becomes larger, but it is reasonable and still works well in practice. To be specific, the prover time of Virgo is O(C +n log n) while both of the proof size and the verification time are O(d log C + log^2 n) for a d-depth circuit with n inputs and C gates. Our scheme only uses lightweight cryptographic primitives such as random oracles and is post-quantum secure. Our implementation of the protocol, Virgo, shows that it only takes 50 seconds to generate a circuit computing a Merkle tree with 256 leaves, at least an order of magnitude faster than existing transparent schemes. The verification time is 50ms, and the proof size is 253KB, both competitive to existing transparent zero-knowledge proof protocols.
Summary. We have introduced Libra, a zero-knowledge proof protocol achieves extremely fast prover time and succinct proof size and verification time. Not only does it have good complexity in terms of asymptotics, but also its actual running time is well within the bounds of enabling realistic applications. Our cryptographic technique can be applied in other application areas such as blockchain technology and privacy-preserving smart contracts. To learn more about Libra, you can read our full paper here. You can view the code here.
We thank Sarah Allen, IC3 Community Manager, for her help in compiling this text.